Coming Soon!, we are working on this site

Artificial Intelligence

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science that deals with building intelligent machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. It involves teaching computers to think, learn and make decisions like humans do. AI technologies include machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing and robotics. AI has vast potential to revolutionize various industries and has already begun to change the way we live, work and interact with each other. However, its rapid development has also raised ethical and safety concerns that need to be addressed.
- Image Recognition: AI is widely used in image processing, where it is able to identify objects, faces, and other elements in images and videos. Applications include photo tagging, object detection, and facial recognition.
- Natural Language Processing: AI can process, understand, and generate human language, leading to new applications in speech recognition, machine translation, sentiment analysis, and more.
- Robotics: AI is increasingly used to control robots in various industries, enabling them to perform complex tasks with precision and speed. This has the potential to improve efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze data from sensors and machines to predict when maintenance is required, reducing downtime and costs. This can be applied in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, transportation, and energy.
- Fraud Detection: AI is used to detect fraudulent activity by analyzing data patterns and detecting anomalies. This helps businesses and financial institutions to quickly identify and prevent fraud, improving security and reducing financial losses.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence that focuses on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computer systems to automatically improve their performance with experience. ML algorithms analyze and learn from data to make predictions, classify information, and make decisions. There are various types of ML, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. ML is applied in various domains such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, recommender systems, and predictive analytics. With the rapid growth of data, ML has become an increasingly important tool to extract insights and automate decision-making processes.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that is based on artificial neural networks with multiple layers. It is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain and is capable of handling complex and large amounts of data. Deep Learning algorithms can perform tasks such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing and game playing. The algorithms learn through iterative training and update their parameters automatically to improve accuracy. Deep Learning is widely used in computer vision, robotics, and natural language processing, among other domains. With advancements in computing power and large amounts of labeled data, Deep Learning has revolutionized many fields and is continuing to drive innovation in AI.
Data Science

Data Science is an interdisciplinary field that involves the extraction of insights and knowledge from data through the use of statistical and computational techniques. It involves the collection, cleaning, analysis, and interpretation of large amounts of data. Data Scientists use techniques such as machine learning, data visualization and statistical modeling to analyze data and make predictions. The goal of Data Science is to extract valuable insights that can inform business decisions and drive innovation. Data Science is used in various domains such as healthcare, finance, marketing and customer service to improve decision making and drive growth. With the growing amount of data generated in today's digital world, the demand for Data Scientists with the skills to turn data into actionable insights is rapidly increasing.
Big Data

Big Data refers to the extremely large and complex data sets that are generated and collected by organizations in today's digital world. These data sets are so large and complex that traditional data processing techniques are inadequate for managing them. Big Data technologies such as Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases are used to process and store these data sets. Big Data has the potential to provide valuable insights and drive innovation in various industries, such as healthcare, finance, and marketing. By analyzing large amounts of data, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior, identify new opportunities, and make informed decisions. However, the management and analysis of Big Data also pose technical and ethical challenges, such as privacy and data security.
BlockChain
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure, transparent and tamper-proof way. It uses cryptography to ensure the integrity and validity of the data stored on the network. Blockchain technology is most famously used as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, but its applications go beyond finance. Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize industries such as supply chain management, voting systems, real estate, and many others, by enabling secure and transparent record-keeping and reducing the need for intermediaries. The decentralized nature of the technology also means that it is resistant to tampering and censorship, making it a secure way to store and transfer data and assets.
Cloud Computing

Cloud Computing is a model for delivering on-demand access to shared computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, over the internet. It allows users to store, process and access data and applications from remote servers rather than having to run them locally on their own devices. Cloud computing offers several benefits, such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and reliability, as users only pay for the resources they use and don't have to worry about maintaining the underlying infrastructure. There are three main types of cloud computing: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Major cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. Cloud computing is rapidly transforming the IT industry and has become a critical component of many organizations' digital strategies.
Networking

Networking refers to the interconnection of devices, such as computers, servers, and smartphones, to allow the exchange of data and communication between them. Networking is critical for the functioning of the internet, as it allows devices to connect and share information. There are several types of networks, including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and wireless networks. Networking protocols, such as TCP/IP, are used to standardize the communication between devices on the network. Networking technologies have become increasingly important in today's connected world, as they support the exchange of information and collaboration both within and between organizations. With the rise of cloud computing and the internet of things (IoT), networking will continue to play a critical role in enabling the seamless exchange of data and communication between devices.
Cyber Security

Cybersecurity refers to the practices and technologies used to protect internet-connected systems, networks, and devices from unauthorized access, theft, and damage. It encompasses a wide range of technologies, processes, and practices that are designed to protect sensitive information, maintain privacy, and ensure the availability and integrity of critical systems. With the increasing number of cyber-attacks and the growing volume of sensitive data being stored and transmitted online, cybersecurity has become a critical issue for individuals, businesses, and governments. The field encompasses many different areas, such as network security, threat intelligence, and incident response. To protect against cyber threats, organizations need to implement strong cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, encryption, and regular software updates, and develop a comprehensive security strategy.
Software Development

Software Development is the process of designing, creating, testing, and maintaining software applications and systems. It involves a wide range of activities, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and deployment. Software development can be done using various programming languages and tools, and follows a software development lifecycle that includes planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. The field of software development is rapidly evolving, driven by the growth of cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Software developers play a critical role in building and maintaining the technology infrastructure that underpins modern society, and there is a growing demand for skilled software developers in a wide range of industries. To be successful in software development, one must have a strong understanding of programming languages, algorithms, and software development methodologies, as well as the ability to think creatively and solve complex problems.
Web Development

Web Development refers to the process of creating, designing, and maintaining websites. It involves a combination of front-end and back-end development, which includes the design and implementation of the user interface, as well as the development of the underlying web application logic. Web developers use a variety of tools and technologies, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and web frameworks, to build and deploy websites. With the growing importance of the internet in commerce, communication, and entertainment, web development has become a critical field, with a growing demand for skilled web developers. Web development encompasses a wide range of activities, including website design, e-commerce development, content management, and search engine optimization. To be successful in web development, one must have a strong understanding of web technologies, as well as the ability to think creatively and solve complex problems.
Mobile Development

Mobile Development refers to the process of creating software applications for mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. It involves the use of mobile operating systems, such as iOS and Android, and requires a deep understanding of the unique design and user experience considerations of mobile devices. Mobile developers use a variety of programming languages and tools, such as Swift, Java, and React Native, to create apps that are optimized for smaller screens and touch-based input. With the increasing importance of mobile devices in our daily lives, mobile development has become a critical field, with a growing demand for skilled mobile developers. Mobile development offers many opportunities for innovation and creativity, as developers strive to create new and engaging apps that meet the needs of a diverse and constantly-evolving mobile market.
Game Development

Game Development is the process of designing, creating, and coding video games. It involves a wide range of skills and disciplines, including game design, programming, art, and audio engineering. Game developers use a variety of tools and technologies, such as Unity, Unreal Engine, and C++, to build and deploy games. The field is constantly evolving, driven by the growth of mobile gaming and the increasing power of gaming hardware. Game development offers many opportunities for creativity and innovation, as developers strive to create new and engaging gaming experiences for players. Success in game development requires a combination of technical skills, creative vision, and the ability to iterate and refine game designs based on player feedback. Game development is a growing and dynamic field, with a growing demand for skilled game developers.
DevOps
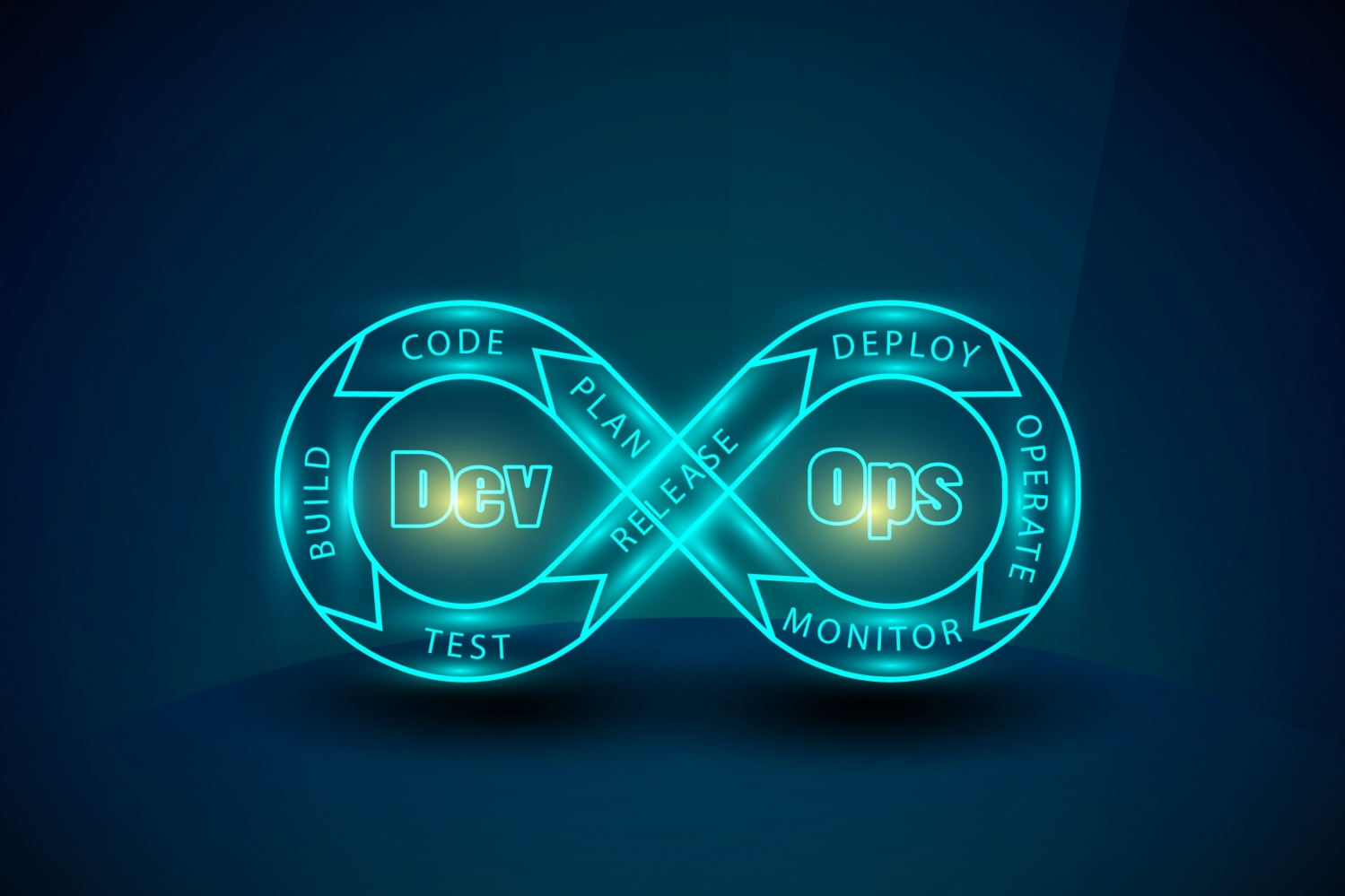

DevOps is a set of practices and culture that aims to bring development and operations teams together, promoting collaboration and communication, to deliver high-quality software applications faster. DevOps emphasizes automation, continuous integration and delivery, and the use of tools such as Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes. DevOps helps to improve software quality, speed up delivery, and reduce downtime and errors. DevOps teams are cross-functional, incorporating developers, testers, and operations personnel, and work closely with stakeholders to ensure software is delivered efficiently and effectively. Adopting DevOps requires a shift in organizational culture and processes, and can bring significant benefits to organizations, including increased efficiency, faster time-to-market, and improved collaboration between teams.
Contact us: rccinternational@gmail.com